Usos y Ventajas de la Estructura de Tracción
July 27,2022
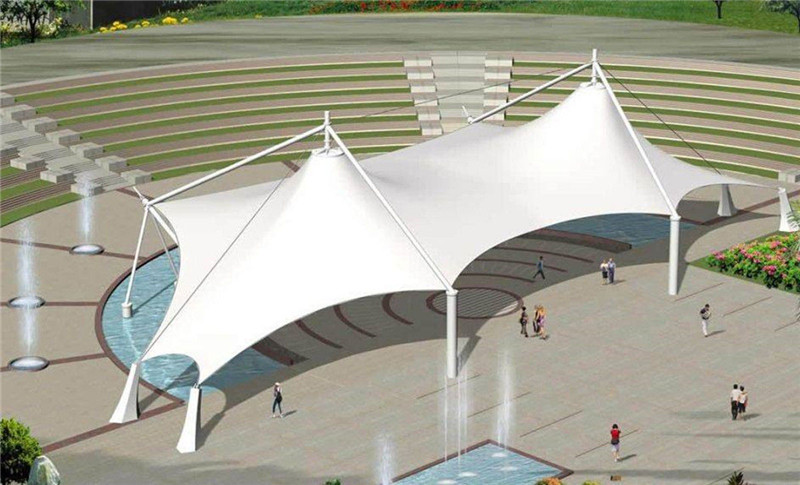

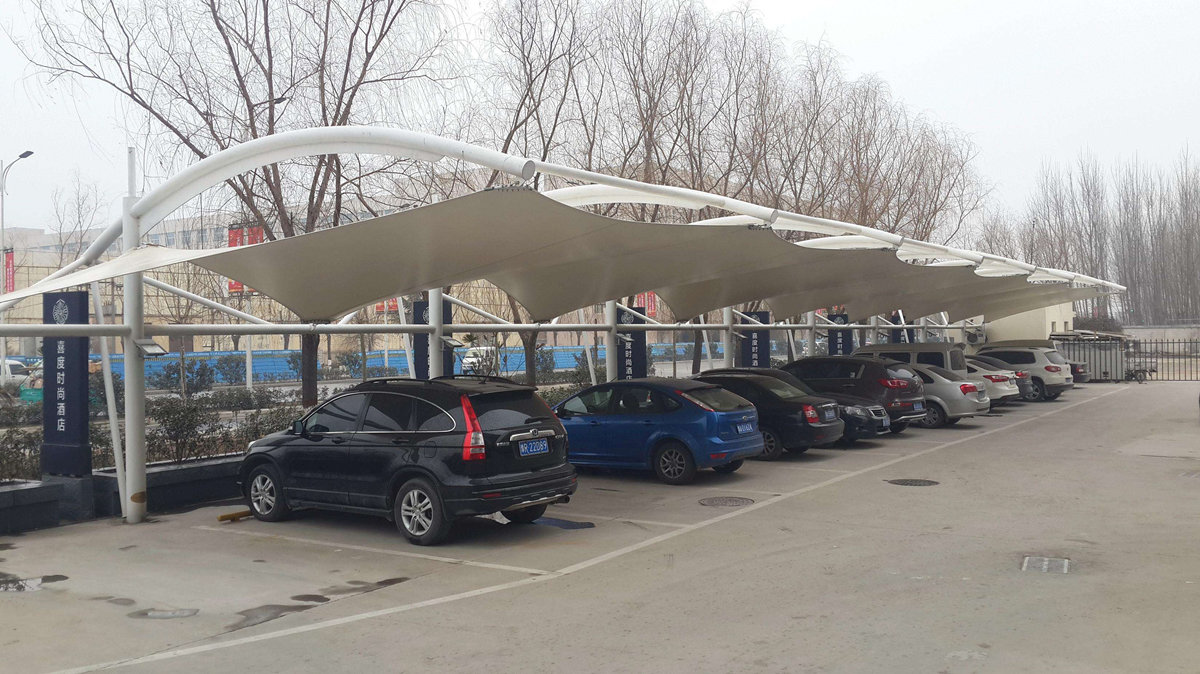
Una estructura extensible es una estructura de tela liviana que transporta cargas utilizando tensión. Stretch Structures Fabric Structures describe varias estructuras de películas estirables y el estado actual del conocimiento. Las estructuras de tela extensible se usan comúnmente en instalaciones de transporte, edificios y otras aplicaciones que requieren un alto grado de sustentabilidad y estética. También se pueden usar como una alternativa liviana a los marcos de acero, como rascacielos, estructuras de sombra para parques infantiles, estructuras de sombra para jardines, etc.

El diseño de estructuras tensadas puede variar dependiendo de las necesidades de un proyecto específico. Suelen utilizarse para dar sombra o dar sombra a las edificaciones. La belleza de las estructuras tensadas las convierte en una opción atractiva para muchos tipos de instalaciones. También ofrecen una combinación única de funcionalidad confiable y atractivo estético. Estos beneficios los convierten en sistemas estructurales muy populares. A continuación se enumeran algunos ejemplos de estructuras de tracción. Las estructuras de tracción se pueden diseñar con áreas grandes o pequeñas. Puede cubrir grandes espacios como lugares para eventos, estadios, lugares de actuación o estructuras militares. Los ejemplos más pequeños incluyen restaurantes al aire libre, bares en la azotea, velas de sombra tensadas y más. La construcción extensible es una opción excelente para aplicaciones en exteriores porque brinda una sensación de exterior y es resistente a la intemperie. Debido a las propiedades únicas de tensión de la membrana, la estructura de tela extensible tiene una forma elegante única. Su translucidez también proporciona una luz natural suave y difusa. La iluminación artificial también se puede utilizar para generar iluminación exterior. Las estructuras tensadas se pueden utilizar para crear edificios modulares prefabricados o como elementos ligeros de estructuras existentes. Son una de las opciones más rentables del mercado. Cuando se diseñan y construyen correctamente, las estructuras de tela extensible pueden ser muy duraderas.
.jpg)
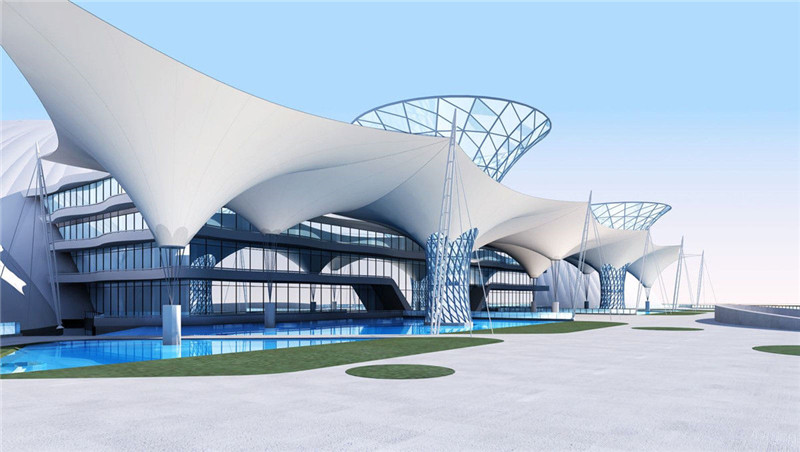
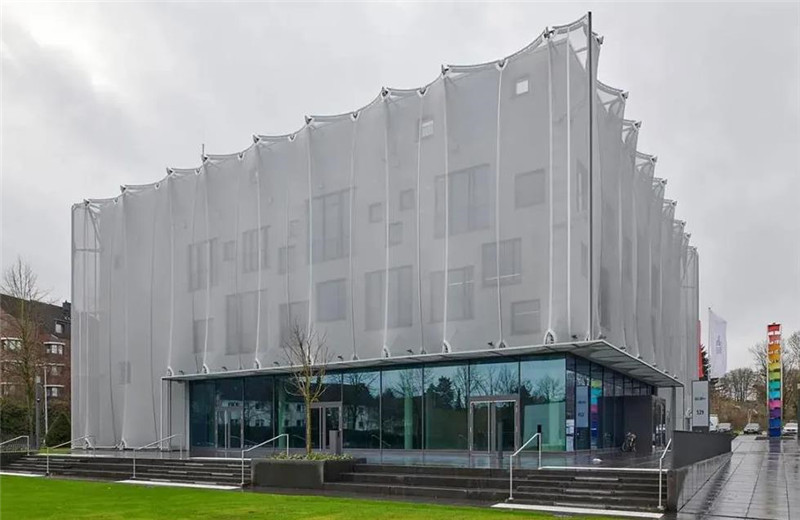
El arquitecto alemán Frei Otto fue una figura fundamental en el desarrollo de la arquitectura de tracción. El trabajo pionero de Frei Otto demuestra que la relación entre la forma arquitectónica y estructural es íntima y mutuamente beneficiosa. El monumental edificio de tracción de Frei Otto, el Hangende Dach en Munich, ganó el Premio Pritzker de Arquitectura 2015. Redefine las estructuras y los sistemas prefabricados y demuestra que son compatibles con el diseño sostenible. Los tejidos elásticos suelen ser combinaciones de fibras utilizadas en diversas aplicaciones. Los detalles de la estructura de tracción tienen muchas ventajas, incluida la capacidad de minimizar el área de superficie entre los puntos. Además, es muy eficiente y maximiza el uso de fibras caras y de alta resistencia. Y como es ligero, también es duradero. Si está buscando estructuras de tracción para su proyecto, ¡contáctenos hoy!
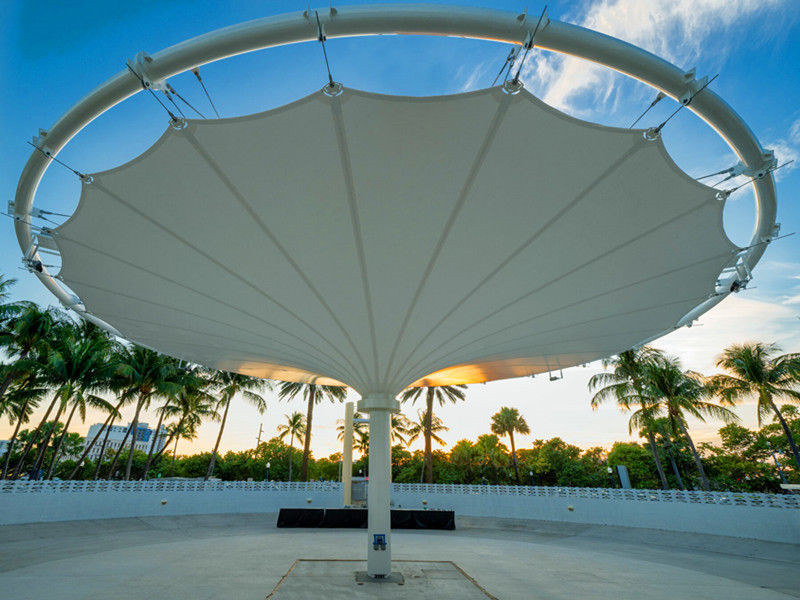

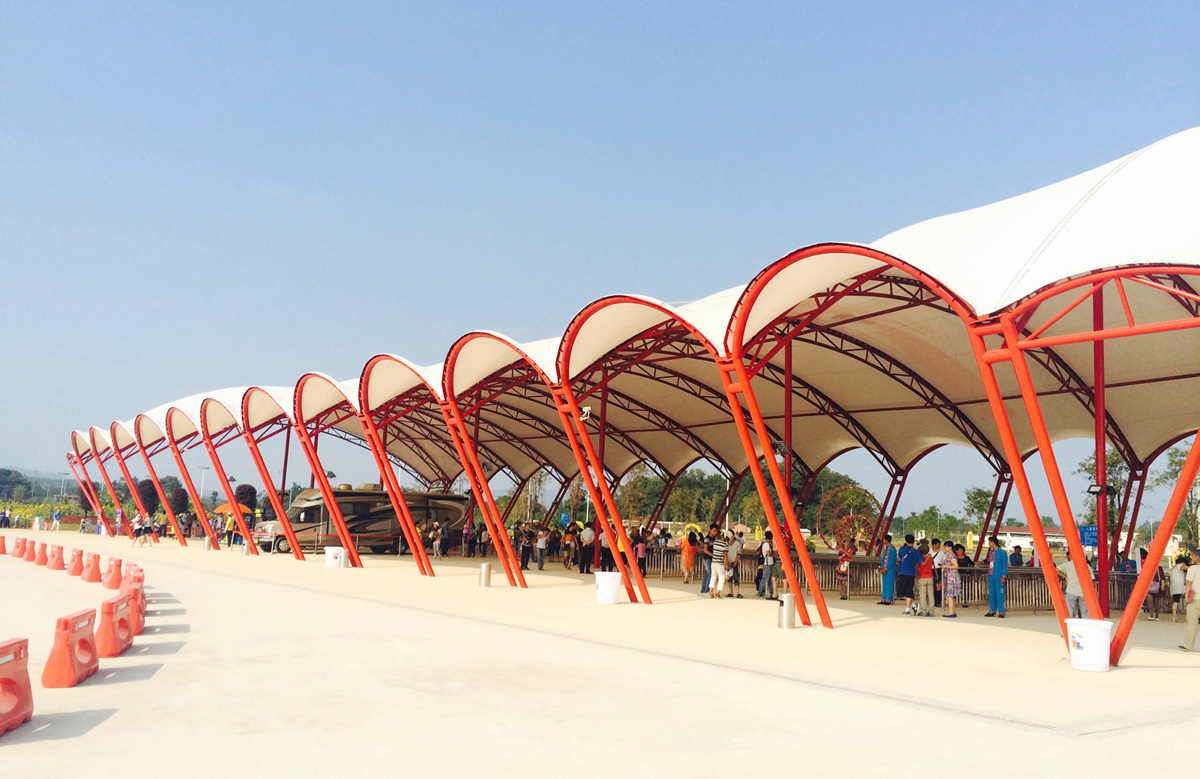
Las estructuras tensadas son más rentables y utilizan menos material que los edificios de tela tensada. Las estructuras tensadas pueden crear edificios completos, lo que las convierte en la primera opción para trabajos de diseño complejos. Las estructuras de tejido extensible suelen estar hechas de tejidos finos que se tiran en direcciones opuestas para crear una doble curvatura. La doble curvatura duplica la rigidez del tejido. Las estructuras de tracción pueden abarcar grandes distancias sin soportes intermedios.
¿Qué es la Estructura de Tensión y Cuáles Son Sus Beneficios?
July 13,2022
.jpg)
El concepto básico detrás de las estructuras de tracción es el uso de telas para crear sistemas estructurales fuertes. Estas estructuras se pueden reforzar con cables de alta resistencia a un costo mucho menor que las estructuras tradicionales de acero u hormigón. Si bien algunas estructuras de tela dependen de dispositivos mecánicos para mantener sus estructuras en su lugar, su dependencia de estos dispositivos puede provocar una deflación preocupante y otros problemas. La creciente aceptación de las estructuras textiles hace que las estructuras textiles tensadas sean un sistema estructural menos controvertido.
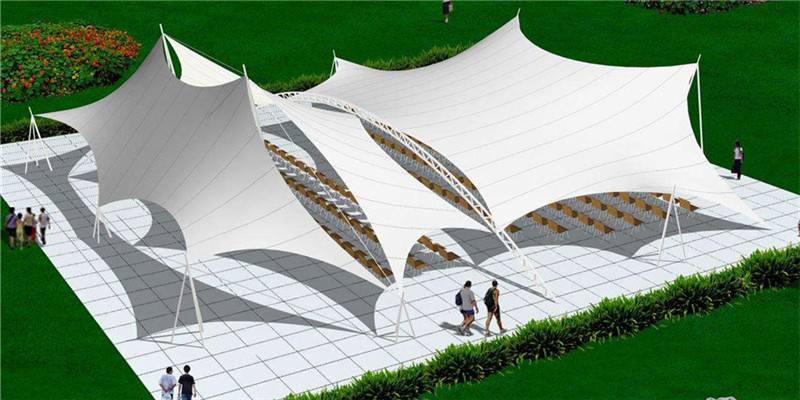

Si bien la arquitectura de tracción es más conocida hoy en día, sus raíces se remontan a la Edad de Hielo. La estepa siberiana alberga asentamientos humanos primitivos hechos de pieles de animales envueltas entre palos de madera. Esta puede ser la primera estructura tensada porque es liviana y fácil de transportar. Eventualmente, los humanos desarrollarán formas de replicar estas estructuras utilizando materiales más eficientes y sostenibles. Hoy en día, el proceso es ampliamente utilizado en grandes edificios. Los edificios de tracción se pueden utilizar como almacenamiento general o instalaciones de gestión de residuos. Sin embargo, los edificios extensibles no pueden diseñarse para incluir ventanas o soportar un techo sólido. Sin embargo, esto no limita las opciones de diseño. En cambio, el marco de acero de la estructura se puede ajustar para crear formas dramáticas. La tela también se puede manipular para obtener efectos visuales interesantes. Esto permite una variedad más amplia de aplicaciones que la construcción convencional.
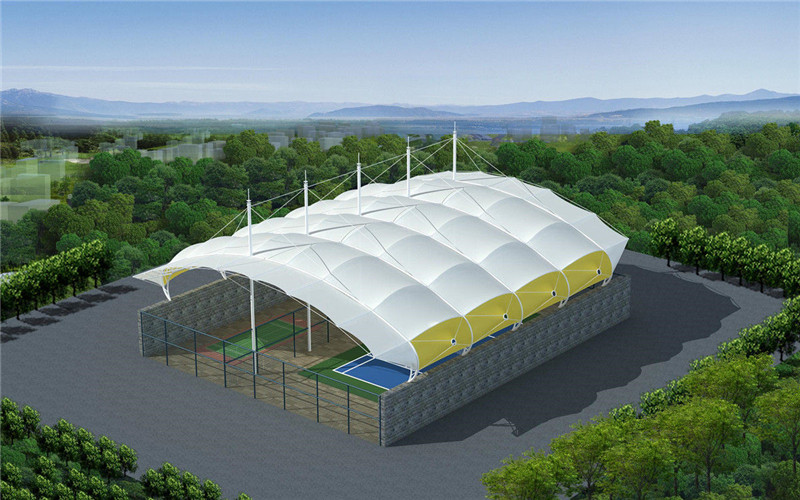

Otro nombre para las estructuras de tensión es estructuras de tejido de tensión. tela de sombra de pérgola retráctil Los edificios de tela de tensión son una estructura liviana, fácil de instalar y pueden abarcar grandes distancias sin la necesidad de columnas internas o postes. Los edificios de tela tensada generalmente incluyen un marco de acero para soporte estructural, y la tela actúa como una cubierta protectora que deja pasar la luz natural y protege de los elementos. Si bien esta construcción tiene la ventaja de poder abarcar grandes distancias, la tela tiene poco espacio para los pliegues y sigue siendo duradera. Ahora, muchos lugares escénicos tendrán edificios que también se pueden usar como estructuras de glorietas permanentes. El estilo es cambiante y también es un edificio icónico. Además de ser estéticamente agradable, la construcción con tejido elástico también es una opción muy económica. Las estructuras de tracción son más fáciles de construir y menos costosas de mantener que las estructuras tradicionales de acero u hormigón. Las estructuras de tela extensible se pueden utilizar en muchas aplicaciones diferentes, desde edificios existentes hasta estructuras independientes. Su geometría única la convierte en una de las estructuras más versátiles y asequibles del mercado.
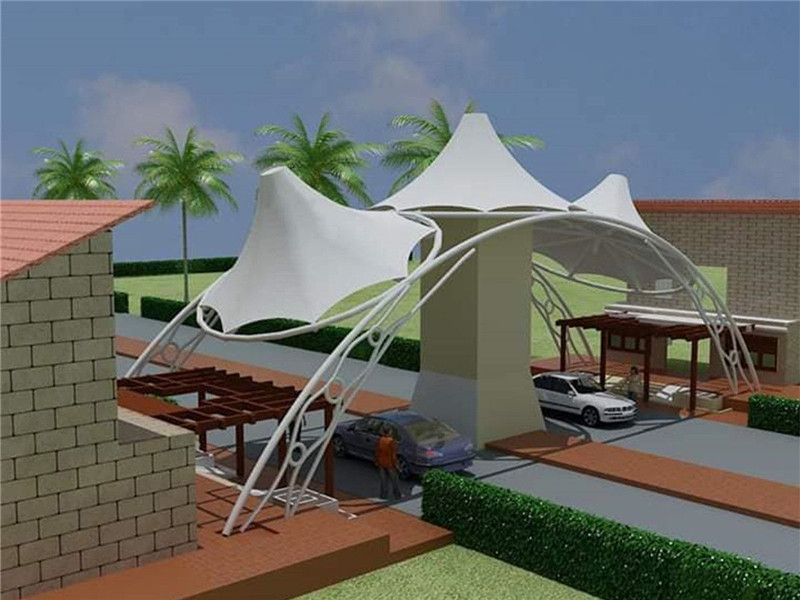

Otro beneficio de los tipos de estructura de tracción es que es altamente reflectante. Proporciona una iluminación más eficiente durante la noche y reduce significativamente las demandas del sistema HVAC. Además, la superficie altamente reflectante del tejido elástico lo hace ideal para dar sombra a fachadas y planos de techo. Los beneficios de esta estructura son innumerables. Puede usarlo como fachada para edificios, estacionamientos o campos deportivos. Los componentes básicos de una construcción de tela elástica son la silla y el cono. Se trata de formas asimétricas que se pueden combinar para satisfacer necesidades específicas. Combinando estos dos componentes, la estructura de tensión puede lograr cualquier forma deseada. Este tipo de estructura se llama pretensado y se puede utilizar en una variedad de aplicaciones. Si está buscando una estructura de tracción simple pero versátil, una silla de montar a prueba de balas le servirá bien.
¿Cuáles son las ventajas de las estructuras de tela extensible sobre los edificios tradicionales?
July 05,2022
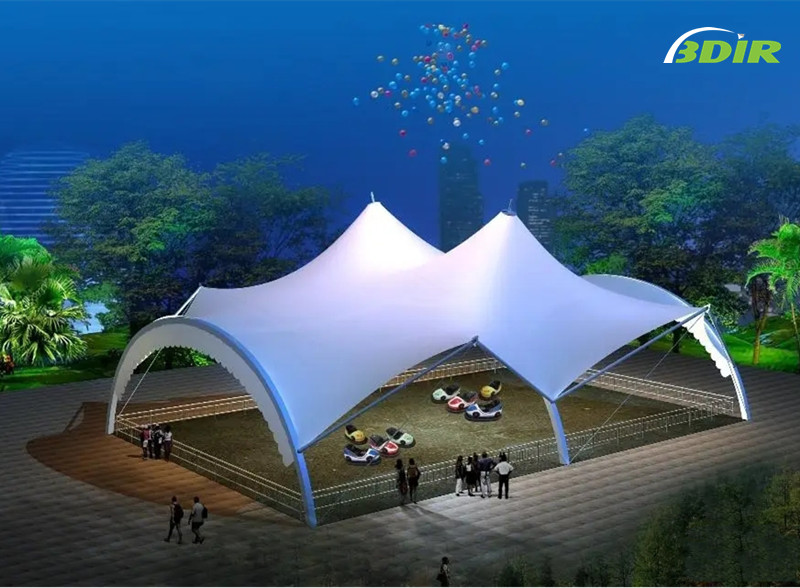

A estructura de tejido de tensión es un edificio que utiliza la tela como estructura para soportar el peso. Llamado a menudo tensile fachadas, estas estructuras se pueden utilizar para cubrir el exterior de edificios, aparcamientos o campos deportivos. La construcción elástica también es ideal para incorporar mensajes de marca en gráficos de tela. He aquí un vistazo más de cerca a los beneficios de la confección con tejido elástico.

estructuras de tejido tensado utiliza dos bloques de construcción básicos: silla de montar y cono. Ambas formas son muy versátiles y se pueden utilizar para crear estructuras que se adapten a sus necesidades. La silla de montar se puede considerar como una cuadrícula torcida de rectángulos, mientras que el cono se parece más a un volcán. Dos tipos de estructuras de tensión de la tela se pueden apilar para crear diseños eficientes. ¡Además, la construcción de tejido elástico puede durar 45 años!

Frei Otto fue uno de los primeros pioneros de la construcción por tracción. Frei Otto descubrió que muchas formas naturales tienen una tensión perfecta y desarrolló un método para conectarlas. Más tarde desarrolló un modelo con jabón. El proceso de desarrollo de este modelo arquitectónico ha dado lugar a numerosas innovaciones en arquitectura extensible. En los años siguientes, cada vez más arquitectos y diseñadores comenzaron a incorporar estructuras de tracción en su trabajo.
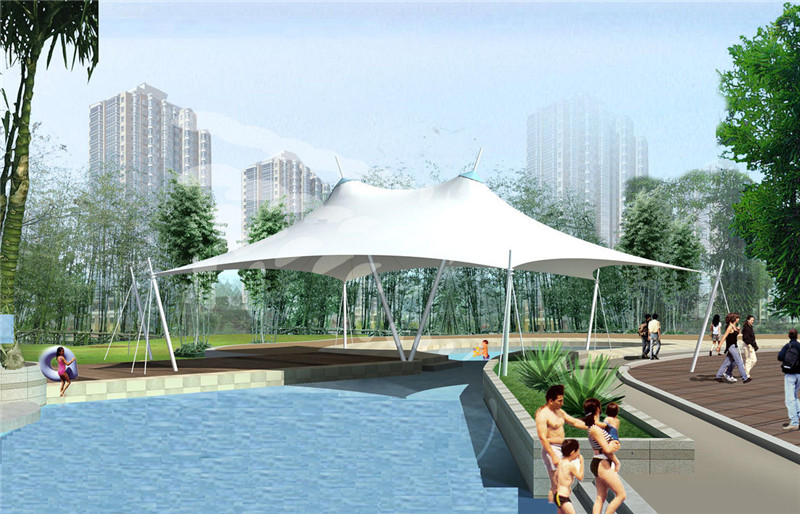

estructuras de tracción son una buena alternativa a las construcciones tradicionales. Como sugiere su nombre, consisten en un marco de metal y una carcasa de tela. En comparación con los edificios tradicionales, las estructuras tensadas utilizan menos material y son más respetuosas con el medio ambiente. El acero es un excelente material de esqueleto y requiere menos material para la estructura que la construcción convencional. ¡En 2014, un edificio extensible con estructura de acero pudo soportar vientos de 130 mph!
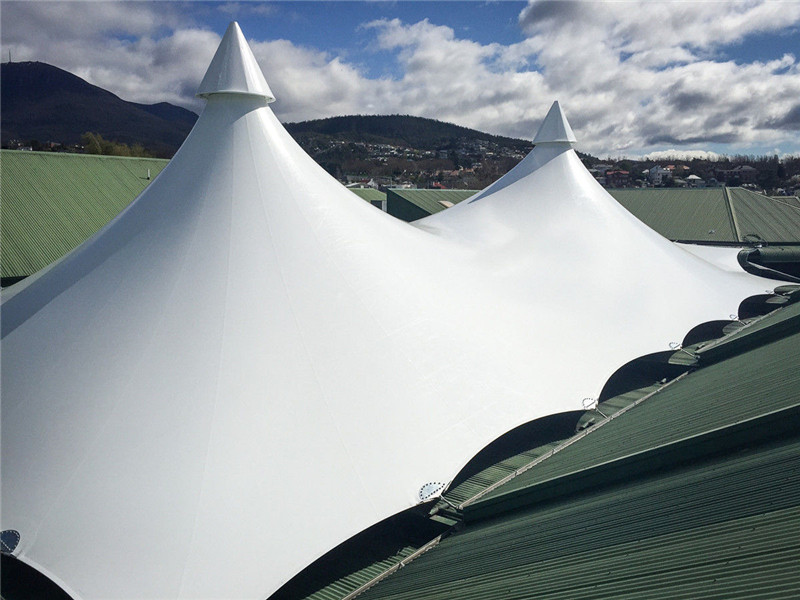

Lo más temprano estructuras de tracción fueron utilizados para refugios exteriores portátiles, tales como tiendas de campaña, refugios. Desde entonces, han seguido evolucionando a medida que diferentes personas utilizaron diferentes materiales, climas y estilos arquitectónicos. Los beduinos y los bereberes usan tiendas de campaña negras, mientras que los moros y los kurdos usan estructuras similares a tiendas de campaña para refugiarse. Entonces, ¿cuáles son las ventajas de las estructuras tensadas sobre los edificios tradicionales?
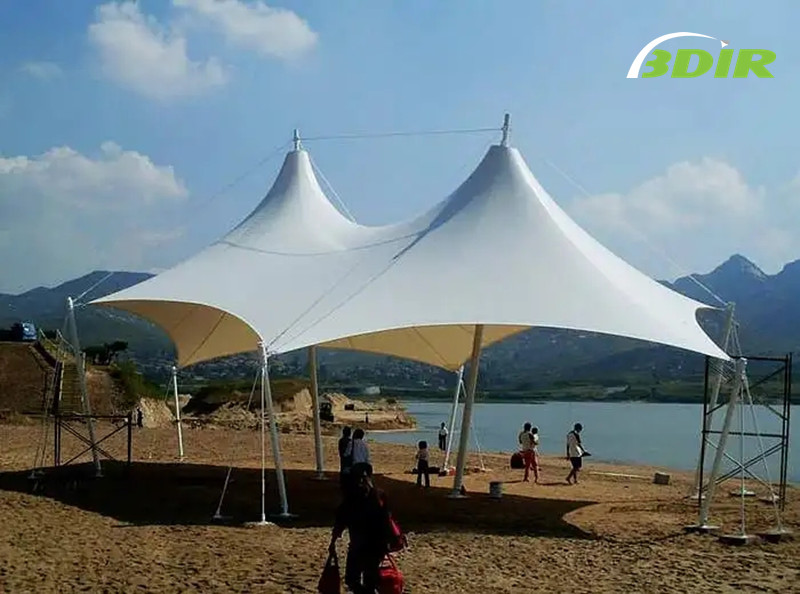

los estructura de tejido de tensión tiene una superficie altamente reflectante para una mejor iluminación incluso durante el día. Esto da como resultado una reducción significativa en la energía requerida para los sistemas de iluminación y HVAC. Esto significa facturas de servicios públicos más bajas para los propietarios de viviendas. La superficie altamente reflectante del estructura de tracción es una gran ventaja para los edificios energéticamente eficientes! Esto lo hace perfecto para edificios y parques. Si planea colocar tensoestructuras en su propiedad, considere los siguientes beneficios:
Las estructuras tensadas utilizan menos material que edificios de tela extensible, y se puede utilizar para construir edificios enteros. Es más fácil de instalar y requiere menos puntales internos que construcción de tela de tensión. Edificios de tela tensada Por lo general, use un marco de acero como soporte estructural y tela como capa protectora para evitar la entrada de elementos. Obtiene todos los beneficios de las estructuras tensadas sin el alto costo de la construcción interior.
Sunshine Valley & China es la primera estructura de membrana de cable
June 16,2022
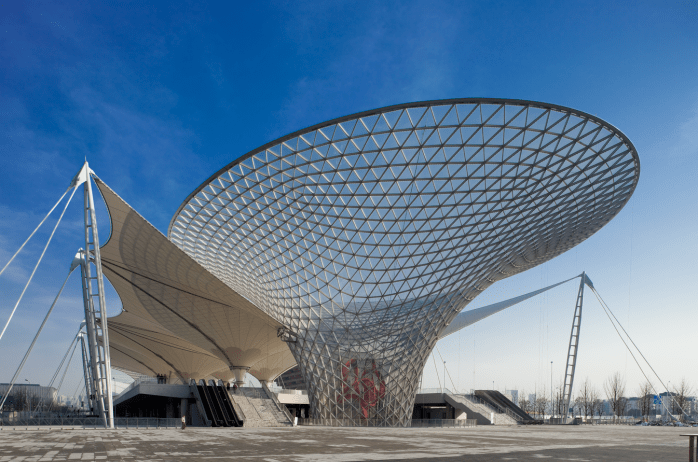

La primera estructura de membrana de cable de China, Sunshine Valley, está ubicada en la fuente de la Expo en el área central del Shanghai World Expo Park. "Aorta". Hablando de los 6 gigantes "Sunshine Valleys", "está compuesto por 13 grandes mástiles, docenas de cables y enormes telas de membrana. Definitivamente es la primera construcción de estructura de cable-membrana en China y rara en el mundo". 6 "Sunshine Valleys" ”, el mayor de los cuales tiene 97 metros de diámetro, y el inferior tiene 20 metros de diámetro, por lo que la pasarela peatonal subterránea del eje Expo de 1000 metros toma prestada luz natural. La estructura especial compuesta por enormes mástiles y tirantes es natural con la tela de membrana blanca gigante.
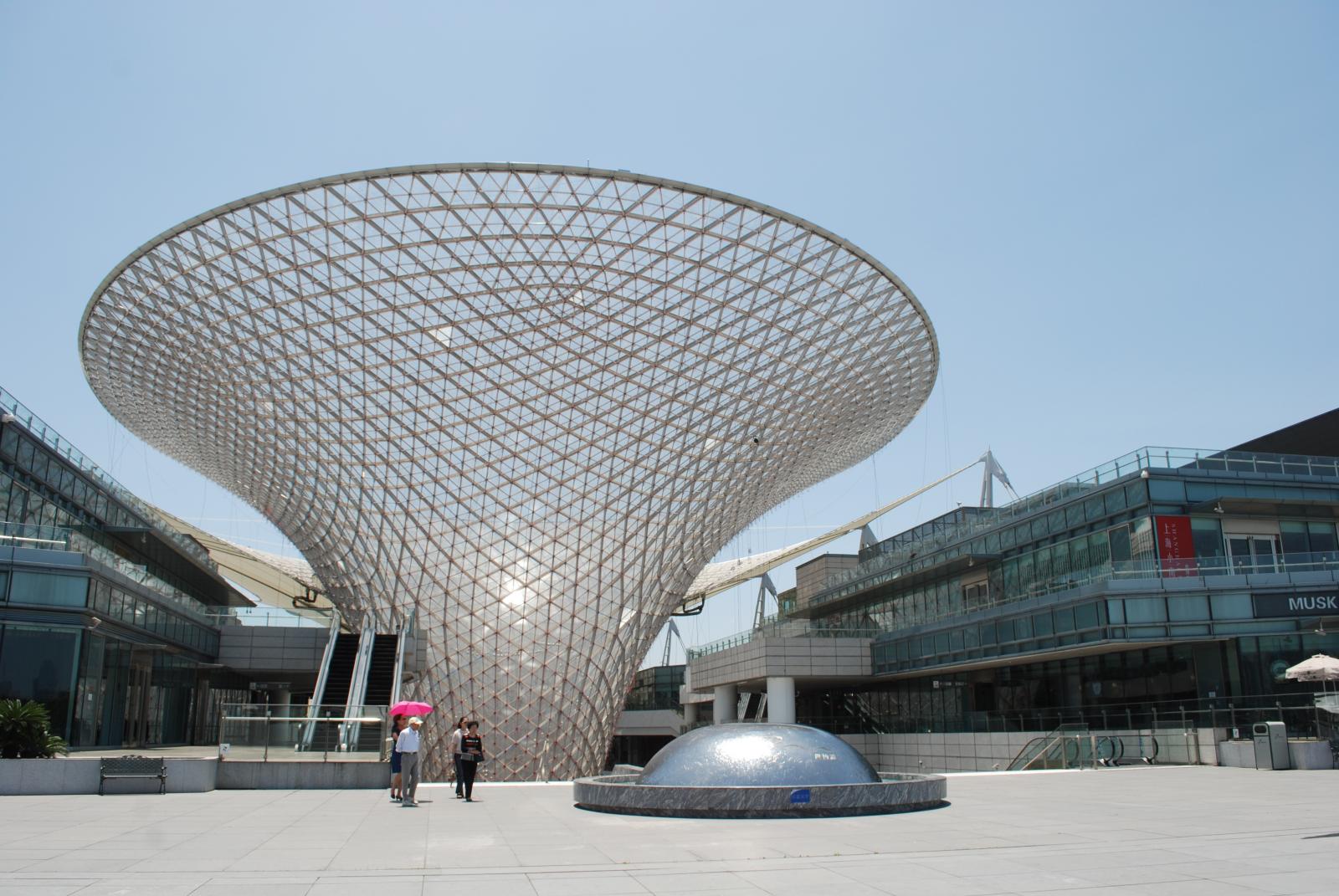

El oleoducto de 250 kilómetros de largo es cálido en invierno y fresco en verano. Expo Axis también es un "campo experimental" para la economía circular de Shanghái. Xu Jun, Gerente Ejecutivo del Proyecto Expo Axis, dijo que se colocó una tubería de 250 kilómetros de largo debajo de Expo Axis para formar una bomba de calor de fuente terrestre. , que se introdujo en el agua del río Huangpu. En verano, el agua del río filtrada se utiliza para formar un sistema de refrigeración, y en invierno, se utiliza un sistema de calefacción con fuente de calor del suelo como fuente principal y agua del río Huangpu como complemento, por lo que que este enorme canal público utiliza los recursos naturales para conseguir calor en invierno y frescor en verano.
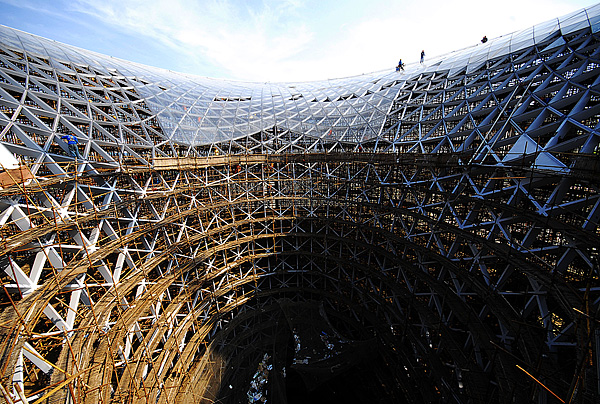

La construcción básica de Sunshine Valley utiliza tubos de acero cuadrados en lugar de tubos redondos. Varios tubos cuadrados se encuentran en el mismo punto, que se denominan "nodos". La forma de malla de la apariencia de Sunshine Valley está conectada por "nodos" de diferentes tamaños. Y cada Sunshine Valley tiene unos 3.000 "nodos", que se pueden calcular pero no se pueden dibujar en los dibujos. los estructura de la membrana en la parte superior adopta la mayor fuerza material de membranal en el mundo, y su tensión de diseño es de 5 toneladas por metro. Dado que no hay pilares en la plataforma del eje Expo, el material de la membrana se basa en 31 mástiles exteriores, 19 mástiles interiores y 817 mástiles interiores. Cuerda de alambre para tirar y tirar uniformemente. Al mismo tiempo, debido a los diferentes tamaños y formas del Sunshine Valley, las posiciones de los nodos de los cables también son diferentes, lo que provoca cambios en la orientación y el ángulo de los cables, que deben resolverse uno por uno durante el construcción.
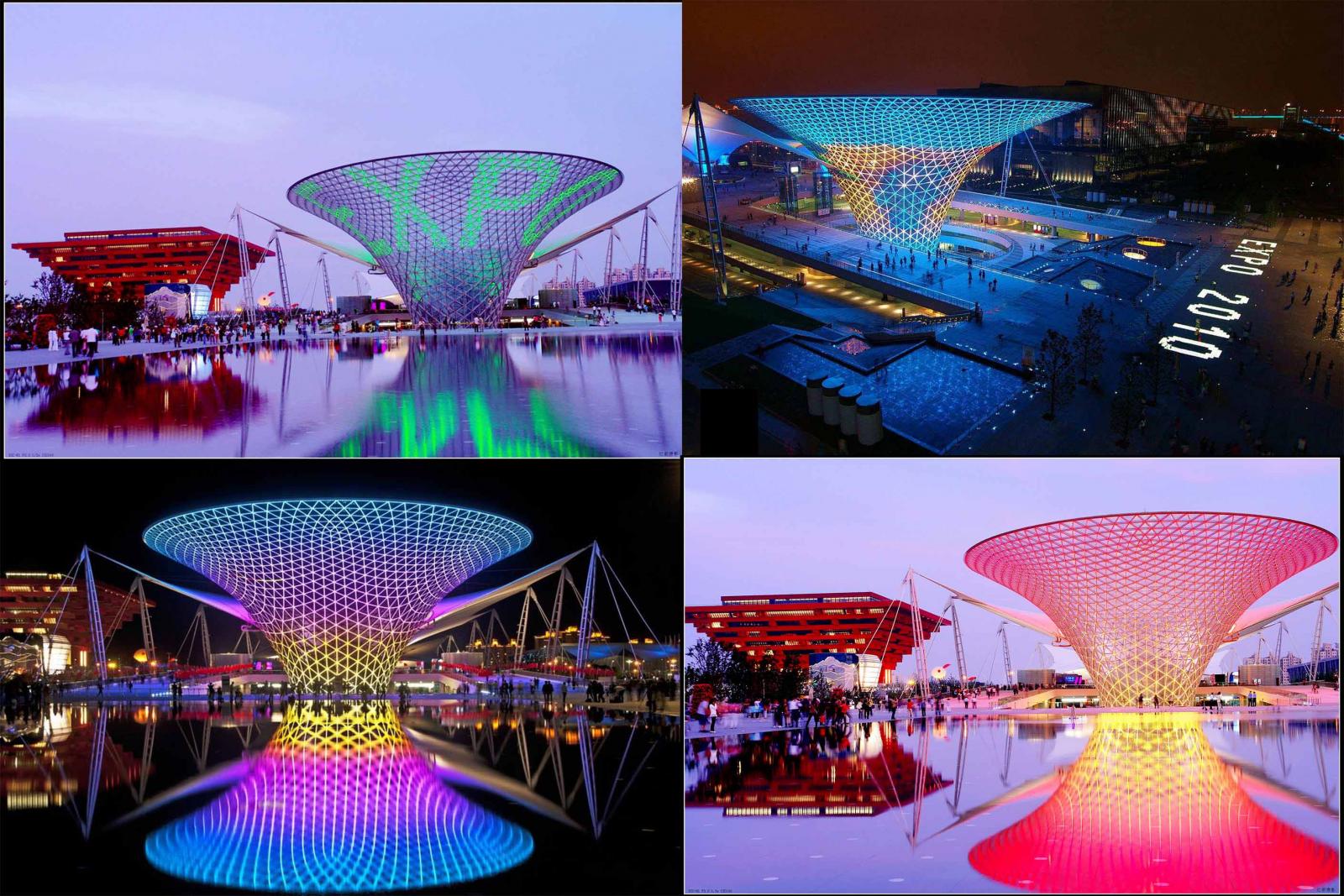

Como el edificio individual más grande de "un eje y cuatro salas" edificios permanentes en el sitio de la Expo, el proyecto del eje de la Expo se transfirió de la construcción de la estructura principal a la etapa de construcción de la decoración, y los cables y lámparas para la iluminación del paisaje se colocaron fuera de la estructura de acero del Sunshine Valley. La Expo Axis y Sunshine Valley por la noche serán más emocionantes.
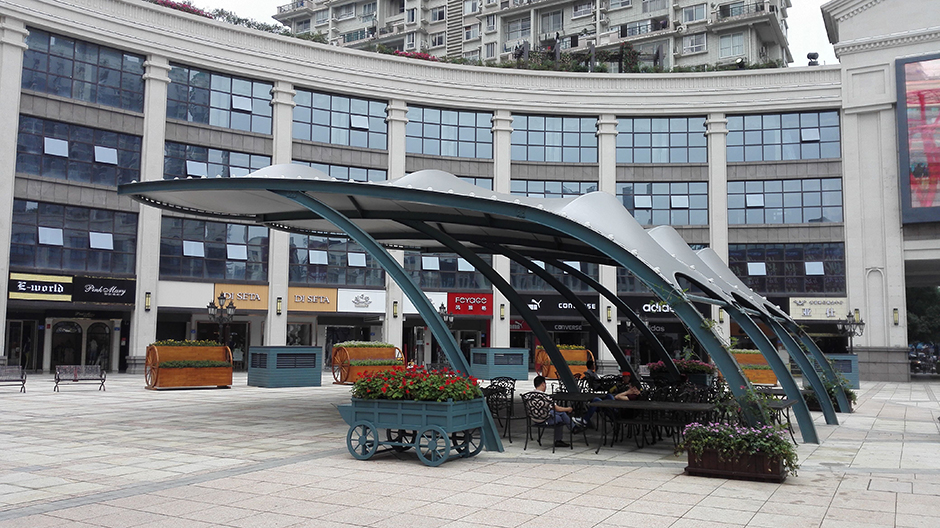
¿Cuál es la diferencia entre una marquesina de estructura de membrana tensada de tela y una marquesina tradicional?
June 28,2022

En aplicaciones prácticas, la carga de la estructura de la membrana pile carport no solo puede proteger la pila de carga, sino también proteger los vehículos debajo de la estructura de la membrana cochera de pila de carga. No solo tiene un estructura de parasol impermeable en el sol y la lluvia y la nieve. Como un nuevo tipo de cochera para pilas de carga, la estructura de la membrana La cochera de pila de carga no solo brinda mucha comodidad a nuestro viaje, sino que también, en comparación con la cochera tradicional, no solo es simple en construcción, sino también muy hermosa en apariencia, estirando La resistencia estructural de los materiales de construcción utilizados en el estructura de la membrana también es muy alto, lo que no solo puede proteger las pilas de carga y los vehículos del viento y la lluvia, sino que también agrega un hermoso color a la ciudad debido a su estética. estructura de la membrana, también conocido como estructura de tela, es ampliamente utilizado no solo en edificios comerciales, instalaciones de transporte, campos deportivos, gimnasios y otros lugares.
Artístico: estructura de membrana Apoyándose en el modelado y el color, puede combinar las condiciones naturales y las costumbres étnicas, y crear formas curvas que son difíciles de lograr en los edificios tradicionales según la creatividad del arquitecto. estructura de membrana es la visión romántica de un arquitecto, disfrutando de un espacio romántico como la naturaleza.

Economía: La estructura de tela tiene una cierta transmisión de luz, que puede reducir la intensidad de la iluminación y el tiempo durante el día, y puede ahorrar energía, lo que también hace que la estructura de la membrana sea un edificio muy ecológico.

Gran envergadura: El estructura de tracción puede superar fundamentalmente las dificultades encontradas por las estructuras tradicionales en la realización de edificios de gran envergadura (sin soporte), crear un gran espacio visual sin obstrucciones y aumentar efectivamente el área utilizable del espacio.

Autolimpieza: los materiales de construcción de acero utilizan membranas con revestimientos protectores, lo que puede hacer que los edificios tengan un buen efecto de autolimpieza y garanticen su vida útil.
Corto plazo de construcción: Debido a la particularidad de la estructura de tensión de la tela, su período de construcción se acorta considerablemente en comparación con los edificios ordinarios, lo que mejora la eficiencia del trabajo
Pabellón de estructura de tela del puente peatonal - un hermoso paisaje en la ciudad
May 19,2022
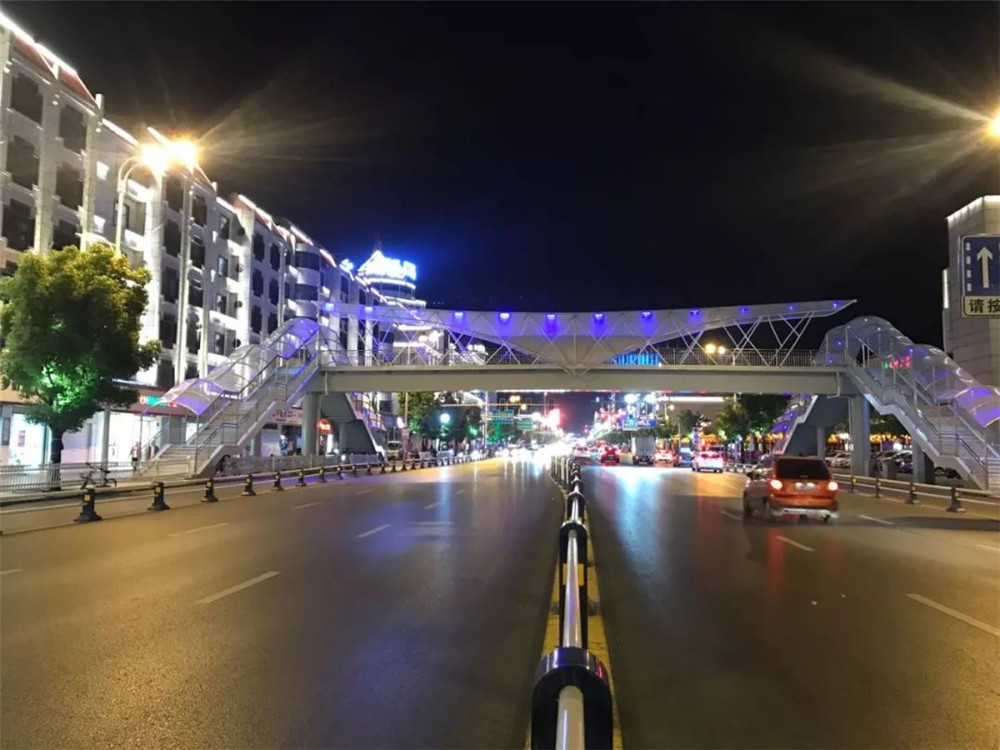

Con el aumento de la población urbana y del flujo vehicular, en áreas densamente pobladas como escuelas, hospitales, plazas comerciales y barrios residenciales, existe una gran demanda de peatones para cruzar la calle, lo que suele entrar en conflicto con el paso normal de vehículos y plantea potencial riesgos para la seguridad. Como resultado, se erigieron pasos elevados a través de la calle, mejorando la eficiencia del tráfico de vehículos y garantizando la seguridad de los peatones que cruzan la calle.
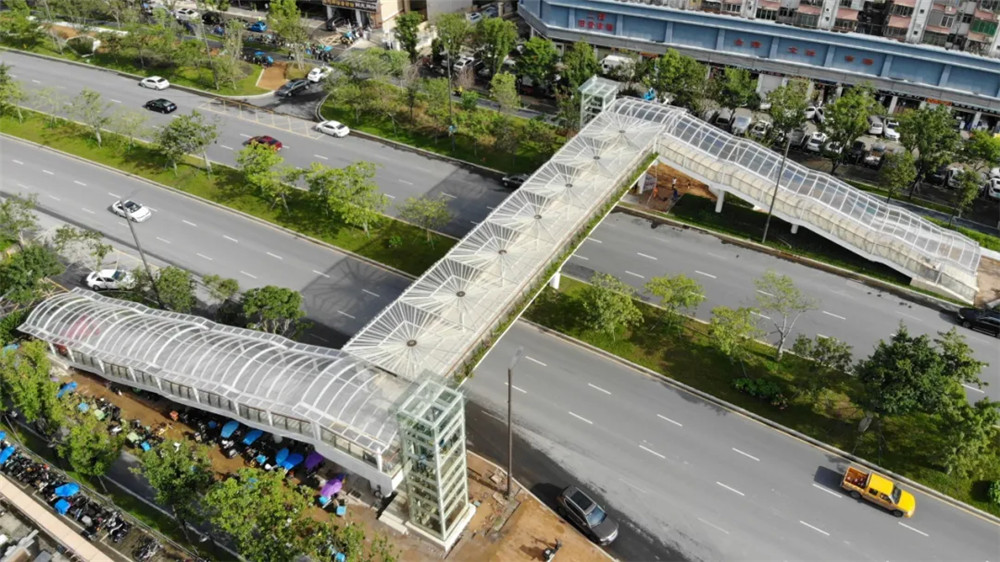

Según la impresión de la gente, los pasos elevados al otro lado de la calle son puentes de acero con barandas, y los más hermosos son los pasos elevados circulares en los cruces. Sin embargo, con el rápido desarrollo de materiales de membrana ETFE, PTFE, PVDF y acero inoxidable y aleaciones de aluminio materiales, las ventajas de las estructuras de membrana se han utilizado plenamente en el diseño y la construcción de pasos elevados, lo que hace que los pasos elevados ya no sean un edificio frío de cruce de calles con una función de tráfico, sino también puentes paisajísticos y puentes de observación que se suman a la temperatura de la ciudad y estilo.
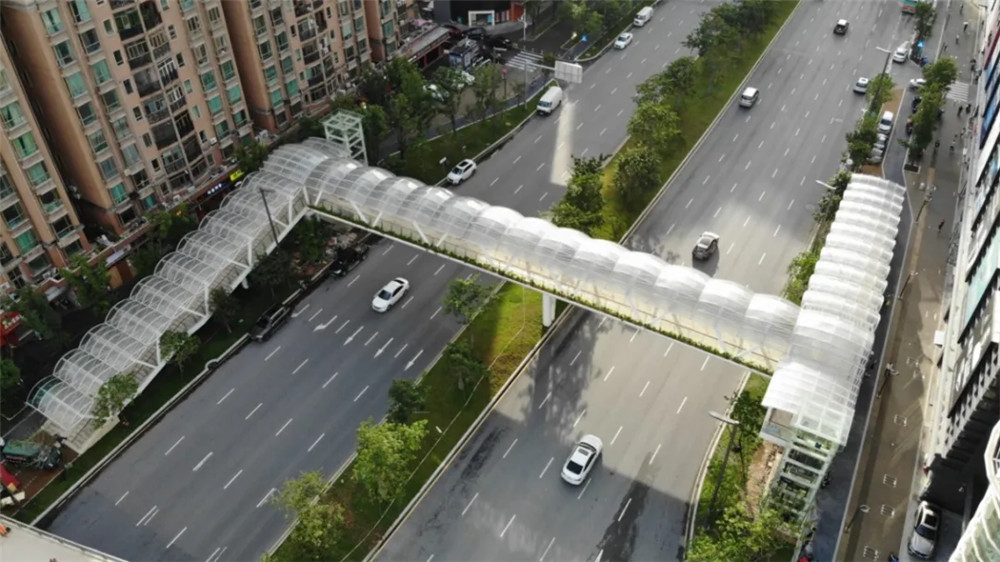

Debido a su forma especial y al desempeño del propio material de la membrana, la estructura de la membrana puede crear ideas de diseño que no pueden lograrse con los sistemas de construcción tradicionales.
¿Por qué las gradas de los estadios usan estructura de membrana y tela?
May 09,2022
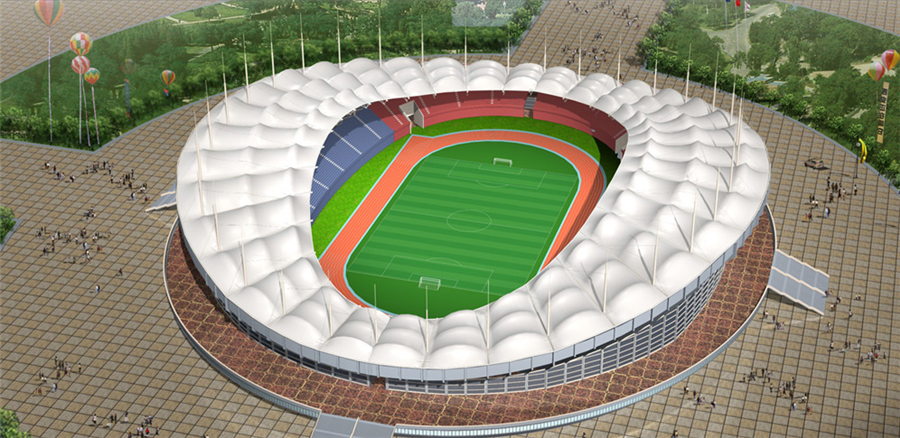

1. La estructura de membrana es un nuevo tipo de material, que es artístico, económico, aislante térmico, autolimpiante, ignífugo, absorbente de sonido y transmisor de luz. El uso de estructura de membrana en gradas deportivas puede reflejar mejor esta característica de estructura de membrana. En comparación con los soportes tradicionales, la estructura de membrana de los soportes deportivos tiene las características de una forma hermosa, espacio amplio, peso ligero y larga vida útil. La estructura de membrana es una nueva forma de estructura de construcción, que integra arquitectura, mecánica estructural, química fina y ciencia de materiales, tecnología informática, etc., y tiene un alto contenido técnico. Su superficie curva se puede cambiar arbitrariamente de acuerdo con las necesidades de diseño del arquitecto, combinadas con el entorno general, para construir un proyecto de imagen icónica. El material de la membrana de la estructura de la membrana del soporte está hecho de tela base de fibra de poliéster o diferentes revestimientos superficiales como PVDF, PVF, PTFE, etc., junto con PVC de alta calidad, que tiene una forma estable y puede soportar una cierta carga de textiles arquitectónicos. Su vida útil varía con los diferentes revestimientos superficiales, generalmente alcanzando los 15-30 años.
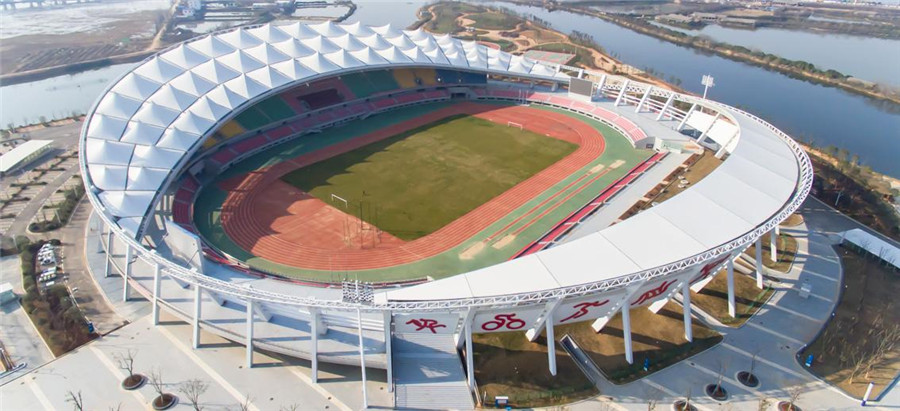

2. Las gradas del estadio con estructura de membrana son hermosas en apariencia y grandes en espacio. Refleja mejor las ventajas del espacio del edificio de la estructura de membrana, y el período de construcción es corto. Las características de las estructuras de membrana han atraído cada vez más la atención y, debido a esto, cada vez más estructuras de membrana están diseñadas para usar estructuras de membrana para reemplazar los edificios de hormigón tradicionales. El peso del techo del edificio de membrana es solo 1/30 del peso del techo de acero convencional, lo que reduce el costo de la pared y la base. Al mismo tiempo, la forma peculiar y el efecto de escena nocturna del edificio de membrana tienen una "visibilidad arquitectónica" y un efecto comercial obvios, y su relación precio-efectividad es mayor.
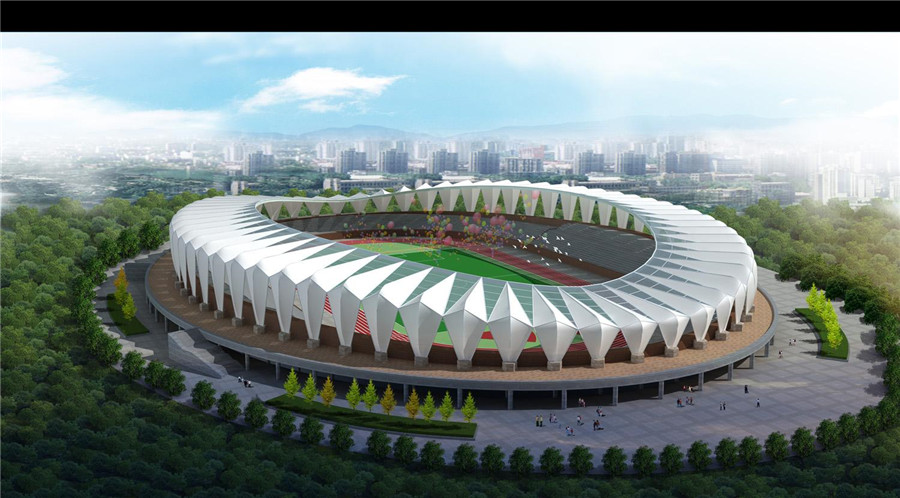

3. El material de la membrana de hermosa forma, los accesorios y sujetadores de acero inoxidable, además del diseño ligero y razonable y el estricto tratamiento de la superficie del soporte de la estructura de acero, crean una estructura de membrana con una forma hermosa y un diseño razonable, que ocupa un lugar importante en el diseño del entorno arquitectónico. alrededor del mundo hoy. posición importante.
¿Por qué el centro comercial Dome & Skylight eligió la estructura de tela?
April 27,2022
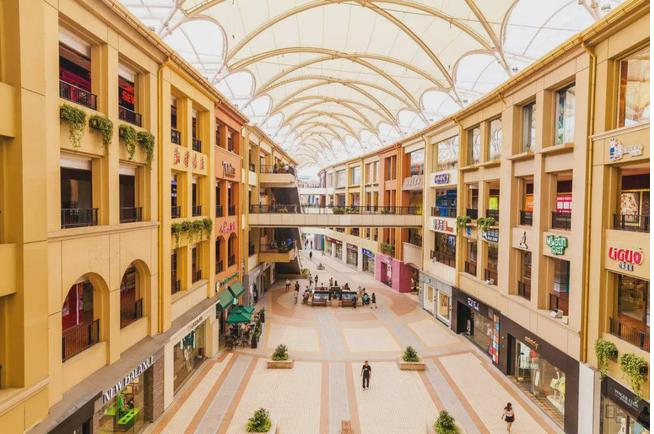

La característica principal de la centro comercial comercial es que la concentración de tiendas comerciales forma espacios interiores y exteriores de compras, ocio, restauración y otros espacios funcionales. La calle peatonal y el área central de actividades son espacios abiertos para que la gente camine, descanse y se comunique. Con base en las características de la calle comercial, se determina que el núcleo de todos los diseños es hacer que el espacio sea más humano.

Como una instalación adicional del edificio, el techo no solo requiere la función práctica de dar sombra y protección contra la lluvia, sino que también debe ser la guinda del pastel. En la actualidad, hay cada vez más casos de ingeniería en los que se utilizan estructuras de membranas textiles en complejos comerciales. Los techos construidos con estructuras de membrana tienen muchas ventajas que los techos tradicionales no tienen.
Los edificios de estructura de membrana son muy populares en aplicaciones comerciales. La capacidad de desmontaje y la gran amplitud de la estructura de la membrana son adecuadas para construir un área de exhibición comercial. Ahora, muchos centros comerciales han utilizado la capa superior exterior de la habitación individual de estructura de membrana, que será única en comparación con la estructura tradicional.
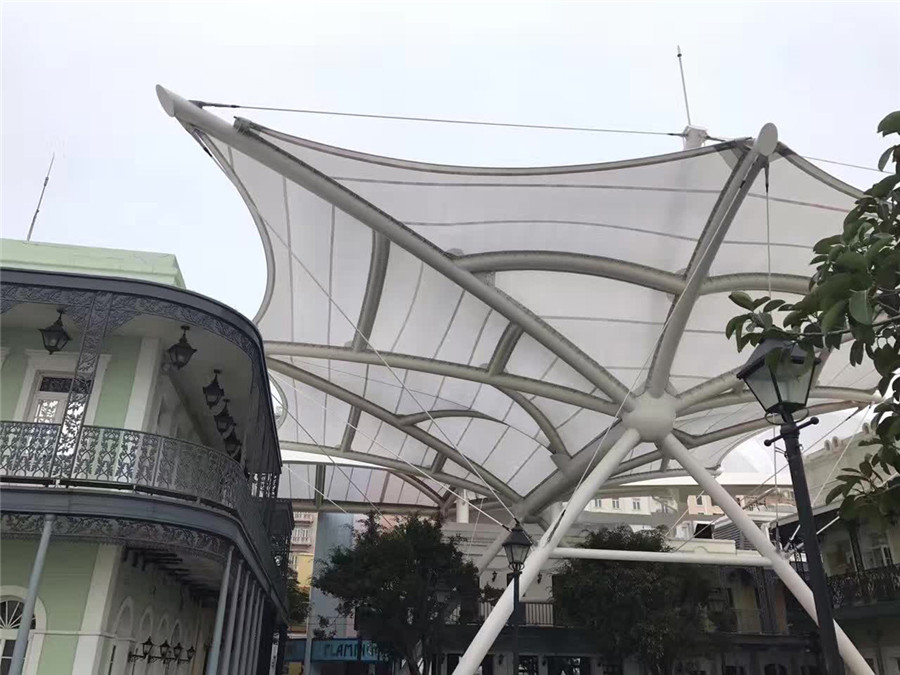

La aparición de la estructura de membrana resuelve varios inconvenientes de los materiales tradicionales. Las membranas de PTFE y ETFE no solo pueden lograr la transmisión de luz, sino también un peso ligero y una mayor seguridad. En particular, las membranas de ETFE pueden lograr una transmisión de luz del 95 % al 100 %, por ejemplo, son tan transparentes como el vidrio, no se requiere iluminación adicional durante el día y ahorran mucho el consumo de energía. Por lo tanto, ha sido adoptado por muchos arquitectos y se ha convertido en la primera opción para bloques comerciales de gran escala.
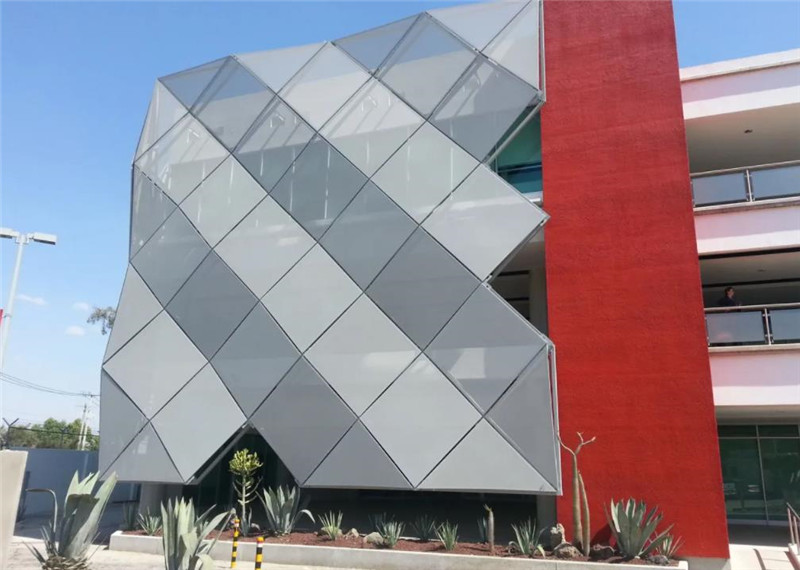
¿Por qué elegir tela para la fachada?
April 25,2022
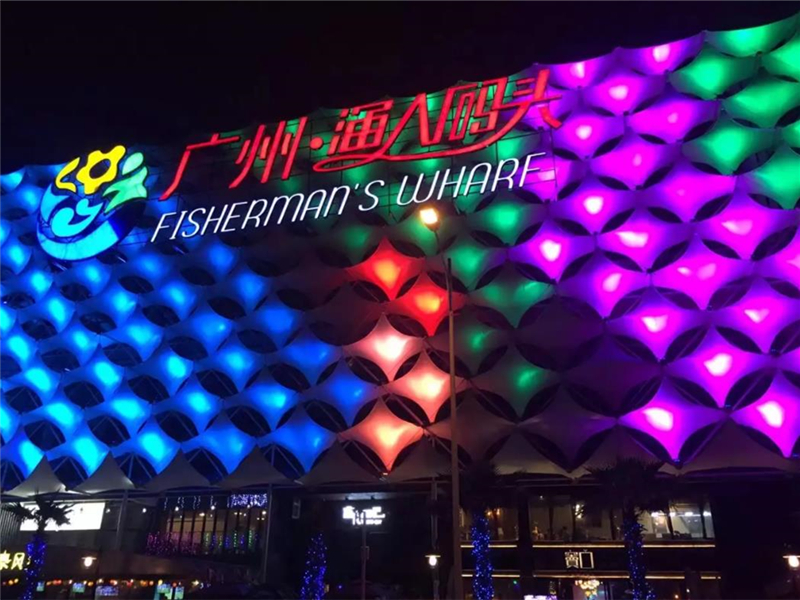

El "muro cortina de tela y fachada" es una solución de fachada de edificio que utiliza materiales de tela flexibles resistentes a la intemperie, combinados con sistemas de marcos, para renovar las fachadas de edificios existentes o diseñar las fachadas de edificios nuevos. Este material puede hacer que el edificio con un gran volumen presente un sentido visual ligero y transparente. Se divide en muro cortina de tela metálica y muro cortina de tela no metálica de material flexible. Su superficie curva se puede cambiar arbitrariamente de acuerdo con las necesidades de diseño del arquitecto, combinadas con el entorno general, para construir un proyecto de imagen icónica.
Aplicación de materiales de tela y tres ventajas principales: teñido ligero, estampado e estampado y modelado arbitrario.

01. Teñido de iluminación: use la luz para cambiar el color de la fachada arbitrariamente, y la fachada de tela cambia la atmósfera con la luz interior, de modo que el edificio ya no sea una cara estática. Además, la tela suave logra una sensación metálica dura.

02. Impresión e impresión por inyección de tinta: sobre la base de una textura metálica perfecta, puede imprimir cualquier patrón que desee. La imprimibilidad de la superficie de la película de malla brinda un espacio creativo para que los diseñadores enriquezcan la forma de la fachada del edificio y resalten la imagen emblemática. El patrón pintado con aerosol no afecta la transparencia de la línea de visión.
.jpg)
03. Forma arbitraria: el material de la membrana se utiliza como proyecto de aplicación de la fachada del edificio, que es un proyecto que utiliza un soporte de cable y un material especial de cortina tensora de perfil de aluminio. Usando la suavidad y la elasticidad de los materiales, se desarrolla el espacio tridimensional y la forma del edificio presenta una variedad de formas, especialmente adecuadas para varios edificios curvos que son difíciles de lograr con otros materiales.
Tensoestructuras Textiles a Medida y de Diseño | Sombrillas de Exterior | Sombrillas Personalizadas
March 17,2022

En un espacio exterior bien iluminado, la sombra de una estructura de sombra es a menudo indispensable, pero el estructura de tracción no es solo la función de dar sombra, sino también un elemento importante en el diseño de exteriores. Un parasol que combina con el entorno no solo puede condensar la atmósfera general del espacio exterior, sino también perfilar el agradable paisaje exterior.
los pantalla de tela Las estructuras de las estructuras al aire libre pueden brindarnos unidad visual y armonía, y también pueden planificar la prioridad superior e inferior en el espacio, creando un "foco". Abierto o cerrado, un paraguas es un paisaje.
hoy estructura de tela el diseño se ha convertido en una moda. Los parasoles con diferentes formas y posturas crean una variedad de estilos para espacios al aire libre. Ya sea simple y moderno, o relajado e informal, o estable y elegante, o mezcla y combinación retro, un paraguas puede enfatizar la personalidad del espacio al aire libre.
La estructura y el diseño de la tela deben ser autónomos con la decoración del espacio exterior y deben estar en armonía con el entorno natural circundante. Es un marcador del hábitat humano y, al mismo tiempo, un hermoso adorno en la naturaleza.

los estructuras de carpa de tela tienen la función de dar sombra, por lo que, naturalmente, brindan a las personas una sensación de "seguridad y estabilidad". Al aire libre, con la existencia del sistema de tensión de la tela, todo el espacio tiene una atmósfera más "hogareña", lo que hace que las personas se sientan más relajadas y cómodas.
Para espacios exteriores, la estructura de sombra no solo se usa durante el día, sino que también proporciona iluminación durante la noche. Las diferentes decoraciones de iluminación también hacen que los paraguas brillen con una atmósfera romántica diferente.
Archivo
Categorías
Novedades en BDiR

Cómo Personalizar tu Propia Tienda Glamping
July 29,2022

Usos y Ventajas de la Estructura de Tracción
July 27,2022

Carpas Domo Geodésicas Aptas Para Vivir y Todo Tipo de Actividades
July 22,2022
Mira nuestros Videos
La tienda ecológica de lujo estructura cabañas para el hotel Tea Garden Holiday
Villas de estructura ecológica de lujo con hospitalidad sostenible